Nuclear Power
Information
Measures against Potential Massive Earthquakes
 Settings of Design Basis Earthquake Ground Motions and Licensing
Status
Settings of Design Basis Earthquake Ground Motions and Licensing
Status
|
Power station |
Conventional DBGEM (reported to the government in March 2009) |
Revised DGBEM approved by NRA |
|---|---|---|
| Takahama | 550gal | 700gal |
| Ohi | 700gal | 856gal |
| Mihama | 750gal | 993gal |
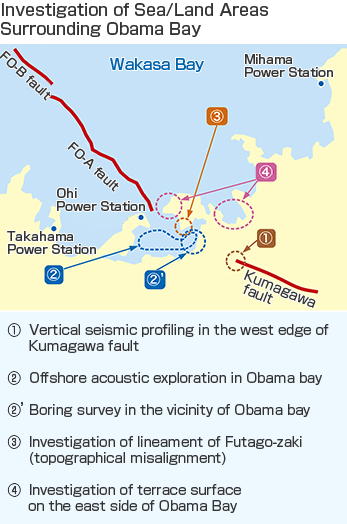
Regarding the setting of design basis earthquake ground motions, we presented plans to take into account the rupture of multiple fault segments, namely FO-A, FO-B, and Kumagawa, and setting the depth of the upper edge of the faults to 3 kilometers below ground level. Based on these plans, we explained that the design basis earthquake ground motion would be 700 gal*1 for Takahama Nuclear Power Station (NPS), 856 gal for Ohi NPS, and 993 gal for Mihama NPS.
Following a review, a license was issued on February 12, 2015 for Takahama, October 5, 2016 for Mihama, and May 24, 2017 for Ohi.
- *1
- Gal: A unit of acceleration which represents the intensity of seismic acceleration of the foundation/building due to an earthquake
Investigation of the F-6 Fracture Zone in the Site of Ohi Nuclear Power Station

Trench surveys, in which trenches are dug to confirm the existence of geological displacements, and boring surveys were implemented in the Ohi NPS site to verify that the F-6 fracture zone is not an active fault.




